Board of Directors of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation 10 September 2021 G. decided to raise the key rate by 25 basis points — up to 6,75% per annum. This decision was motivated by the theme, that annual inflation in August rose to 6,68%, as well as increased the main annual and monthly (seasonally adjusted) indicators of stable price dynamics.
Factors of inflation growth
The data published by the Central Bank indicate a gradual increase in inflation in 2021 G. with 5,38% in March until 6,68% in August.
According to the Central Bank, this is because, that "demand for goods continued to expand faster than supply, which, along with rising producer costs, was exerted by proinflationary pressures".
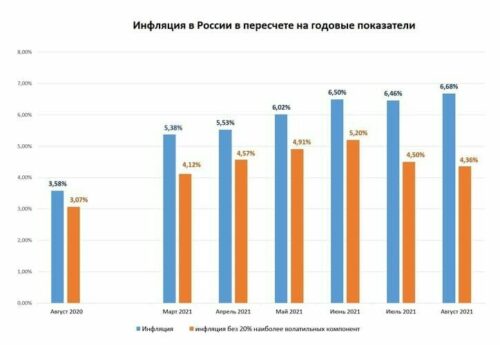
Rice. 1. Inflation rate in Russia. A source: data of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation Rice. 1. Inflation rate in Russia. A source: data of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation
The Central Bank approves, that the increase in inflation was facilitated by emergency spending to combat the pandemic and support the economy in the face of sanitary measures., temporary closure of borders and other factors. As a result, the budget deficit of the Russian Federation in 2020 G. made up 4,1 trillion rub. (3,9% GDP), and in 2021 G. the expected deficit will be about 1% GDP. The assessment was given in June by the Minister of Finance of the Russian Federation Anton Siluanov during the St. Petersburg International Economic Forum. Earlier when approving the budget 2021 G. it contained a deficit 2,75 RUB trillion, or 2,4% GDP. But this was done in anticipation of a fall in GDP in 2021 G. approximately on 10% from level 2020 G. In fact, the pace of recovery of the Russian economy was higher., it has almost already recouped the pandemic-induced drop and, according to Siluanov, "the actual execution of the budget was better than expected. This result was achieved primarily due to a more dynamic flow of non-oil and gas revenues.".
Non-monetary inflation
According to many experts, inflation in Russia is non-monetary in nature. First of all, this applies to imported goods, as consumer, and components. If there is a shortage of chips on the world market and the electronics used in the automotive industry have risen in price, costs of Russian automakers will increase under any monetary policy of the Central Bank. Furthermore, if, in conditions of access to cheap credit, individual participants can reduce their margins in the struggle for market share, in the situation of an increase in the key rate and a rise in the price of loans, such behavior becomes less likely. At the same time, the cost of domestic lending in Russia for production is too high., and most of our companies do not have the opportunity to borrow abroad, or such a possibility is limited by sanctions and concerns, that are associated with them.
Why prices are rising?
If the prices of some goods have risen in the global market, they are beginning to rise domestically as well.. And the government has to take extraordinary measures., to break this dependence (for example, impose restrictions on the export of gasoline or grain). At the same time, the logic of the actions of private companies is quite understandable.: they strive to maximize profits and, if exports yield greater profitability, prefer to redirect their products abroad. Or raise prices within the country in accordance with the global situation. To this, they are pushed by the need to obtain international ratings for listing their shares on foreign exchanges and for obtaining loans from Western banks.. If they do not raise the prices of products within the country, the assessment of the profitability of their assets will be lower, than foreign competitors, and this will affect the quotations of shares and the cost of loans attracted by them (and it is more profitable to borrow abroad - Russian loans due to the policy of the Central Bank are too expensive).
monetary inflation
Let's look at inflation indicators from this angle., calculated without taking into account 20% the most volatile components, that is, without taking into account raw materials and industrial products, which are most strongly dependent on the conjuncture of world markets. Share in these 20% Commodities, the price of which is related to the situation in the domestic market and is not related to the global situation, — mala. According to the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, inflation, calculated on stable commodity headings (Appreciably lower, than general inflation), Reduced, starting from June 2021 G. It can be assumed, that it is determined largely by monetary factors., which means, in the latest actions of the Central Bank to raise the rate there was no such urgent need.
What will the increase in the key rate lead to??
Raising the key rate will not lead to a decrease in inflation. But it will have a negative impact on economic growth., which should already slow down after the russian economy reaches the pre-pandemic level and the opening of foreign resorts.
On the other hand, critical braking will not occur. The main obstacles to growth in the Russian economy are the lack of investment and the limited domestic market.. In the foreign market, Russian companies have to face unfair competition in the form of political sanctions, anti-dumping investigations, the upcoming introduction of a carbon tax and the possible recognition of Russia as a country with a non-market economy.
In these conditions, the mechanisms for stimulating economic growth will be non-monetary in nature and should not be highly dependent on the monetary policy of the Central Bank.. And the role of the Central Bank will be limited to the stabilization of the ruble exchange rate and supervision of the banking sector.. At the same time, the banking sector no longer needs to be "cleansed", as a result of which a huge number of small and medium-sized banks were deprived of their licenses, and in creating conditions for meaningful participation of banks in the investment process. But so far, the proposed measures of the Central Bank against the creation of banks' own ecosystems impede bank investments in the economy..
What are the actions of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation aimed at??
In the II quarter 2021 G. the Russian economy has reached pre-pandemic levels and, according to the Bank of Russia, returns to balanced growth. The contribution to inflation from sustainable factors remains significant due to the faster expansion of demand compared to the possibility of increasing output. Under these conditions and taking into account high inflation expectations, the balance of risks for inflation is shifted towards pro-inflationary. This can lead to a longer upward deviation of inflation from the target.. The monetary policy pursued by the Bank of Russia is aimed at limiting this risk and returning inflation to 4%.



