schedule
The Monty Hall paradox and risk management
reminded about . ()
if ugly then
1) you have three doors to choose from, there is a prize behind one of the doors.
2) you make a choice – probability of getting a prize = 1/3
3) after you have made a choice (but none of the doors are open yet) they open the door for you, behind which there is definitely no prize and ask, do you want to change your choice now.
4) it is obvious that now there are only two doors in front of you and the probability of receiving a prize is now 1/2, which is higher than 1/3. (simplifying a little, in the language of probability it will be prettier)
this whole thing is called a paradox because, what most people think, that an open door does not carry additional information, so there is no point in changing the choice. in terms of probabilities – the choice needs to be changed, because 1/2 this is better, how 1/3.
in fact, it's a paradox of a paradox.
in real conditions two choices 1 door from 3, and than 1 door from 2 – are independent. since the choice is made randomly in principle, so it is correct to run your random generator again and point to one of the two remaining doors randomly (if you point to the same, as for the first time – then you don't change the choice, if on another – then change). thus, the formation of the problem conditions leads to a composition error and we focus on formulas instead of reality;)
ie. you make two independent choices, therefore, asking the question `` to change or not to change the decision" leads to an erroneous perception of reality. if anyone knows empirical experiments – share, sure, that the result will be unexpected. can it be like this: the strategy of randomly choosing one of the two doors will outperform the strategy of constantly choosing a `` new door ''.
economists and quanta love to fall for such things. the most striking example of the discrepancy between theory and reality (of those at hand) described by William Feller flipping a coin (popularization from Mandelbrot).
we toss a coin. if the eagle – we write +1 dollars, tail – minus dollar. tossing results are summed up. on shorts (sorry for the quality, photo by phone page from the naughty marketplace" Mandelbrot) third graph – this is the result after 10000 tossing. On the top chart – First 500, second from 500 to 5000.
as we see, if we bet on, that in the long run, our result will tend to zero (what in theory) we may face a situation where market tossing `` goes against us ''. this is where LTCM flew. managers believed, that the spreads will converge. and the spreads converged in the end. but these 'deviations from zero" proved to be sufficient, to knock LTCM out of the saddle.
the practical conclusion is – what is risk management – is the ability to make a decision about, that it's time to change the principle of decision making. for example LTCM – fix losses having felt, that the situation is out of control.
all in all, no one is going anywhere from the need to make decisions on their own.
update.
with the independence of choice in Monty Hall, I seem to be too clever. apparently I was not able to express the idea concretely enough, so the criticism fell on, which is so clear. but, from the choice of 1 out of 2, you can go to the choice of 1 out of 3 and do the same algorithm as in Monty Hole. then the treated probability 2/3 will be higher than the initial probability 1/2 at the initial choice of 1 of them 2. ie. the math trick itself is universally applicable. although it is not known at the practical level whether the strategy of Monty-Hall will outplay the strategy of 2 equal random choices (because of, what is critical is the random distribution of the position of the prize and the door in repeated experiments).
Again, that I did not dispute and do not dispute the validity of the paradox. I thought, what is the focus in specific conditions, but he's in mathematical logic, which consists in reducing the unknown. and, the more we reduce the initial probability (for example, turning choice 1 from 2 to choose 1 from the 10th) the greater the statistical advantage we get when we change the choice.
so i was wrong,
but the fact that I was not shown an error is a consequence of the poor-quality formulation of my idea.
about zero probability of recession
I think, that many have seen a graph of the likelihood of a recession ()
Krugman is good , which affects the instruments / indicators that are used for calculations. there is a fairly common set, including the `` slope of the yield curve ''. when long stakes are higher than short stakes – this is a sign of a normal situation, when the short ones get to the long ones – the loud step of the approaching recession.
I don't quite agree either, what in our case hides behind the normal shape of the curve, something more than normalization of processes. not ready to jump into distant conclusions about, that monetary policy is not working now, but she's definitely not what she was before.
go back a year. how many of you / us believed in high inflation today, or into sustained deflation in 2008 also in 2007 year? who believed in that, that the current rates on long-term securities will be at this level in 2009? some respected people generally like to write about the bubble in the US government debt market (bubble, not a pyramid, which is not the same).
United Kingdom
The Office for Budget Responsibility is created in Britain (GIANT) – this (not)dependent organization (sorry, I could not resist. I can't believe that, that this is not a political move) which will issue budget forecasts. Here , and here they are . The document is large and takes time to read. At the moment it is important to know, that the forecast for economic growth was underestimated (pier, the previous government deliberately inflated forecasts. somewhere we already heard it ..). By the way, tax revenues improved slightly, which slightly reduced the need to issue debt, what the markets liked very much.
Here is a basic prediction.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
What you want to pay attention to first of all, this is the GDP gap.
As seen from the graph, previous prediction of the bad guys" was slightly worse. At this point we turn to the second British topic. – Inflation.
For now, a few words about the GDP gap. Much of the gap calculation is based on unemployment. But, in post-boom periods, some jobs go away forever, What means, that the full load of resources based on the new structure of the economy will be less, than when basing on the old pre-bubble structure.
From here – Central Bank expects, that inflation will be low since the GDP gap is large. If the Central Bank overestimates the size of the negative gap, then the reaction to inflationary pressures will be belated. By the way, this is the most real reason to be afraid of high inflation., not monetary – look in the forum, afraid, but we don't think.
What happens to inflation.
1) The Barclays Survey of Inflation Expectations (BASIX) – inflation expectations survey showed, what are the british waiting for 3,4% in a year, in two years 3,8% what is the maximum with 1995 of the year.
2) UK inflation will be published tomorrow, all kinds of rumors are crawling around the market about, that rising expectations – this is what pushes inflation up, therefore the Bank of England will think and do something.
and now, from the Bank of England – a graph of how expectations and actual figures compare (By the way, for the US, expectations are even less useful).
___________________________________________________________________________________________________
And the third. (short-term financing facility for the non-financial sector)!
The Bank itself said:
Although there were no asset purchases financed by central bank reserves, the Bank continued to purchase sterling commercial paper and operate as a buyer and seller in the sterling corporate bond market, with net purchases financed by the issuance of Treasury bills.
Ie. no QE, just needed to support the market in difficult times. But still, interestingly;)
GDP gap in Asia
as always, accidentally stumbled upon a chart, under which there were several thoughts.
do not like 2 pieces:
1) Asian Central Banks stubbornly look at other Central Banks, no one in asia wants to raise rates before, how the FED will do it (why is that – I don't know, but this is how all investment houses have been writing since autumn 09 of the year. No, of course there is sound logic in this, but just to be so fanatical ..). if rate hikes in the developed world are pushed back a couple of quarters (which, by the way, is also not so obvious), then the rate hike in Asia may be postponed. for the sake of mercy, it should be noted, that besides directly rates, there are many ways to tighten monetary / fiscal policy.
2) there may be problems with counting it and it is underestimated. for example, we take the loading of production facilities in China and consider, that she should be at least 80%. maybe, in fact, there's only 30-40 – this is already the norm, because some of them are a) just go to junk, b) set up in advance. eventually, the real gap is already much higher. (in developed economies vice versa, there is a risk of overestimating the GDP gap).
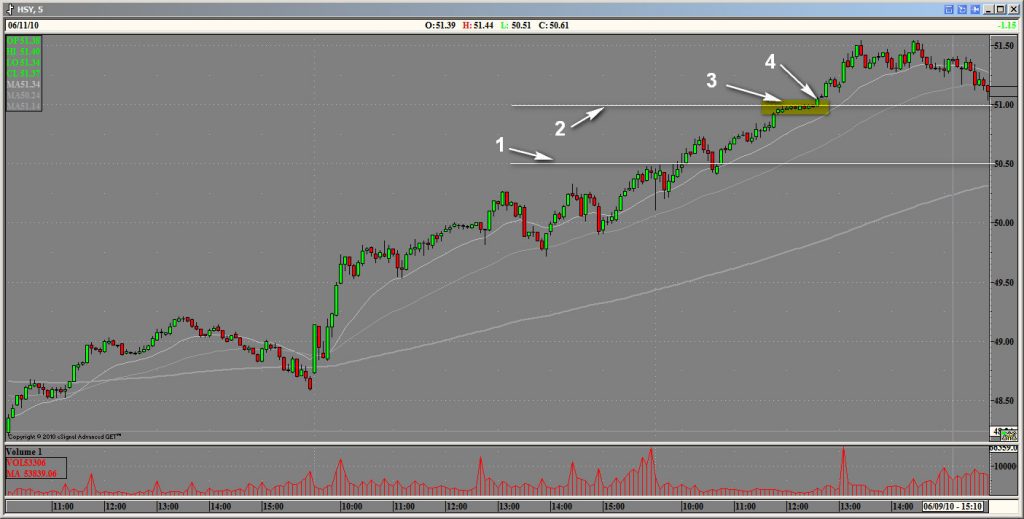
Clairvoyance by Tom Joseph
Here is the monthly schedule SP-500. All signs for the 5th wave down. The only clue may be a small PTI (Total 26), when it must be higher to confirm a high probability of a correct wave 33. Often, with so little PTI, the fifth waves are not completed until the end(failed waves) or appear as double tops and troughs. So that, there is a ghostly hope that the next round of the world crisis will choke halfway.
margins indicate a bull market
City drew a chart with the margins of non-financial companies, comparing them for some reason with Wilshire 5000 Index (with what to compare the difference, in principle, of course not, but why exactly?)).
The conclusion is as follows – early to predict a bear market, and the growth of margins, if you cleanse the financial sector (this is my guess) has the potential. Everything is beautiful, everything is correct, offset.
And some reasoning about unemployment. Generally, for disillusionment in numbers remained little noticed then, what you should have looked at – a sluggish labor market is reviving at a relatively fast pace. PMI shows no deterioration, the private sector still generates something, etc..
But there is a claim to the schedule. The feature of the latest recession is not the number of cuts, and in the low number of job creation. (). Number of layoffs, like the unemployment rate – not indicative without attention to detail. For example, last month, US unemployment rose – and it was very good, now decreased – and this is very bad.
Doubts about system portfolios.
Here I feel that among the systemists there is an opinion that a portfolio of systems for one or related instruments will smooth out drawdowns and give more even profit, that is, you get a smoothly growing graph. Although I use many systems myself, but from a non-mathematics point of view, and life experience there are doubts about this. Well, yes, on history, you can mathematically select a set of such systems, which will smooth out the total drawdown and smooth out the total equity as much as possible. But history rarely repeats itself, and in the next instant after testing, a new countdown will already start with completely different optimal parameters.. Where it used to be smoothed, can, on the contrary, increase the failure, where was the growth, there may be a fall and other manifestations of an efficient market.
Here is for comparison, for example, which equity will be smoother — first option, if we play toss with only one opponent, or, second option, at the same time with ten? To my mind, chance will act here.
That is, it is impossible to predict which equity will be smoother. — on the portfolio of systems, or on one system. Although I want to believe the opposite, because, remind, that I play a portfolio of systems myself.
Someone will say — this is how opposite systems should be played, for example, trend and counter-trend. Yes, in this case, really, in theory, drawdowns of one system should be smoothed by another system. But there is one catch — for example, on futures, only trend systems work and merge counter-trend. I will immediately insert two caveats — we are talking about American futures and stocks not lower than daily(I don't know about the Russians) and about my personal experience in systems building (maybe someone came up with a counter-trend system for futures, but not me). And on stocks and stock indices, vice versa, counter-trend systems work and merge trend. So that, the result of combining trend and counter-trend systems into a common portfolio for trading related assets will bring zero result.
I repeat, these are not statements, but only my doubts, since I don't know the answer to this question. This doubt is based on real life experience of gambling., but not theoretical mathematics, since my knowledge in mathematics is limited to the elementary operations of multiplication and subtraction :)
Trade on paper: a waste of time or a sound teaching method?
During numerous discussions trade on paper and its implications as a learning tool, we usually see participants, divided into two camps. The first speaks of the total uselessness of paper trading., another vows not to start trading without it. Mocking Camp Points to Obvious Limitations of the Paper Trade:
- It does not allow to evaluate slippage during trading.
- This leaves unanswered the question of whether, does your order the ability to be fulfilled at all.
- It keeps you in a relatively relaxed state of mind., since there is no pressure, endangering real money.
- It also prevents you from fully mastering your tools. aboutsending orders.
- Finally, it's very easy to fool yourself, changing the decision after the completion of the transaction and adjusting the results.
Let's try and build trading rules on paper, which will enable us to turn it into a powerful learning tool. We can identify three cases, where paper trading is used instead of real for the purpose:
- Newbie, kicking water.
- Trader, testing a new trading system.
- Trader, fallen into the losing streak.
Trading on paper makes it easier for you in real trading and see if your theoretical approach works. This is the stage, where you start to measure your method against market movements. You will have ample time to review psychological pressure and performance techniques later on., adding them gradually, since you start trading with low volume. but, before real money is used, theory must be verified by reality, and this first experiment should be painless for your trading account, насколько это возможно. Obviously, trading on paper does not pursue any meaningful goals, if your trading system is built this way, that you can test it, thus, starting by building your trading approach, and then continuing testing it in the mode real time.
Trading on paper is built in a fairly simple way. This is a simulation of your actions without actually sending your orders to the market maker. You define your setup with all its components: signal for the entrance, stop level, signs for exit, the possibility of partial exit and pull-ups. Then, watching market action, you simulate your ins and outs, writing them down. This will be your first meeting with the market, so take it seriously. Trading on paper teaches you a lot about market action without scouring your money., if you follow closely and act responsibly.
Watch, do your setups. If you are losing money on paper day in and day out, there is something wrong with your approach. Try to make corrections, find what factors you did not consider. This is the stage of fixing errors - looking for problems to fix. If you receive a negative result, don't be discouraged - it is much better to know about the problem before transferring real money to a dubious method.
Watch, does yours work risk management. You lose within your defined limits on any trade and on any day? Maintain discipline at this stage - your future trading results will be at risk, unless discipline has become your second nature.
The all-important purpose of paper trading is, to figure out the maximum rollback, which you may encounter. This element may require a slightly longer paper trading stage.. The fact, that losses and wins are not necessarily evenly distributed on your trading chart. You may face a string of losses. Although the average loss may be affordable in terms of your trading capital, and the group of losses cannot. It is very important to make sure, that a losing streak doesn't kick you out of the game.
Here are the rules for trading on paper, which allow it to be as close to real as possible and make paper trading an effective learning tool:
- Make your decisions only in real time, not post factum. Looking at the chart and deciding where you can go in and out, you will not do yourself any good. Everything is elementary in hindsight and looks very different., when you're opposite - what Alan Farley calls a hard right edge - end of the live graph, putting you in the dark. Record your entry, when your setup worked, write the output, when the chart reaches your target or stop.
- Follow your trading rules the same way, as if you are trading real money. Any solution like “I will do so, although with real money i will do it wrong” makes trading on paper worthless. If your stop level is reached, trading on paper must be terminated and recorded, even if the stock immediately bounced back. If your exit order is not reached, do not record the result with little profit – it negates paper trading, which should show if your goals are realistic and if the stops are placed correctly.
- Make trades with the same risk, as if you were trading real money. The decision to trade risky stocks on paper does not make sense, at a time when you are not going to trade them on a real account. Your paper trading tests your trading strategy, not a game.
- Use the same set of tools, which you intend to use in real trading. For example, if your trading system requires Level2, then trading on paper without it, with the thought that in real trading with Level2 your trade will be better, makes no sense. She won't get better, everything will be completely different.
- Consider your ins and outs done, only if there are real prints at the target price. Just see bids or asks, which you want, does not guarantee, that you will receive your executed order at this price.
- Determine the number of shares, available at your price. If you are going to trade in 1.000 шерс, but there is only 100 Shares, then most likely in real trading your order will not be fully executed. See real prints, to determine how many shares there really are.
- Don't use paper trading to plan the amount of money, which are you going to earn. This is not the task of this stage.. This can make you overly impatient and eager to start a real trade before you are ready.. just write the results, to see if your strategy works.
Explore your platform. Manipulate settings, change the number of shares, the price of your order, order type and router type. Switch limit order on market order and vice versa, practice changing quickly change cent. manipulate the settings long enough, to make this process automatic. Learn how to place additional orders.
AND, finally, configure sending orders in this way, to keep your money safe. Do it in the following way.
Set a small number of shares – from 10 to 50. Set a price, far enough from the market price, not to be fulfilled. If the stock is trading for about $20, prepare your buy order by $10 and for sale by $30. Submit orders. look, is there any confirmation. Now cancel the orders and see the confirmation. Make Sure, that all messages, which you got, verified, so as not to waste time reading them later. Make Sure, that pop-up notification windows do not interfere with work. Monitor the accuracy of quotes, especially during the most active periods. Make Sure, that you have a phone number, for quick communication with the broker and with the technical support of the provider, in case of possible problems with the Internet.
Often asked, how long should this stage take. But there is no answer, the same for all. There are traders, who study during the week, and I know a broker, who traded on paper for a whole year. This does not mean, that he is a slow learner. He was just perfecting his trading system., until I was completely satisfied. Although the year, maybe, this is already extreme, and a week or two is also not quite right, which suits most people. The exact time is usually not important, since it will be different for everyone. Paper trading has specific goals, and you must move forward, when these goals are achieved. Keeping all your trading rules, you can show a stable profit? You have seen how your setups work and you are comfortable with them? Are you sure you know the drawdown, which your system can create and can withstand this drawdown? You feel comfortable working with charts and trading platform? If you can answer YES to all of these questions, then trading on paper can last only weeks for you. If you cannot answer for any reason, make in practice one of the most important elements of your psychological transformation – patience. Learning to sit on the sidelines will serve you well.. It will also allow you to gain a greater sense of self-control on your first day..
We mentioned two more cases, when paper trading makes sense.
Testing a new system or improvement of the existing, will obviously make you go back to paper trading. You change something – why risk real money before, how to make sure it works well? Usually, when a trader does it, he already has enough experience in his belt, to know how effective trading on paper is. Just make sure, that you are giving her enough time and your results are already statistically significant. I know a trader, which makes this type of new testing setup without stopping real trading. In the process of real trading, it simultaneously records optimized trades, comparing the results and drawing conclusions about the quality of optimization.
After going through a series of losses, the trader wants to find out the reason for the low performance. These are market conditions, which change this way, that it destroys his trading system? This is a trader, who acts unruly himself? If this is a market, whether it has changed fundamentally or is it a short-term fluke? Or changed main trend? Or is it just temporary narrowing the range without volumes? What is likely to happen next? These types of questions are not easy to answer in the heat of battle.. In this way, digression towards revaluation of things, to regroup and rebuild trust or reconfigure your approach, is a good solution.
If for some reason you switch to paper trading, your main step to ensure success in this, is the definition of goals and the development of steps to achieve it.