On the Internet and on television, you can often find references to the "Big Mac Index" in relation to the economic state of a particular country.. We decided to deal with that, how this index came about and what it is actually used for.
History
The Big Mac Index first appeared in September 1986 years in an article by Pam Woodall (Pam Woodall) for The Economist magazine. Изначально это был полушутливый пример инструмента для оценки рынка валют.
The index is based on the theory of purchasing power parity, that is, about the equal value of a basket of goods in different countries. In this case, the set of products was replaced with a popular burger from the menu. McDonald’s. The index has become so popular, which continues to be updated and published so far.
For example, if a set of the same goods is in Germany 10 euros, and in the UK - 5 Pounds, then their ratio should be 2:1, that is, the fair exchange rate will be two euros for one pound, if we conditionally omit transportation costs. If, in some case, such a ratio does not converge with real indicators, means, the selected currency is undervalued or overvalued.
How many burgers can you buy at $50 in a particular country (the full picture will open by clicking)
There are McDonald's restaurants in many countries of the world, therefore, the authors of the index chose the "Big Mac" with a universal composition of products as one of the most common and suitable benchmarks for assessing the ratio of exchange rates.
Why all this is needed
IN 1967 year for "Big Mac" asked 47 Cents. IN 1968 year, it spread throughout the United States and cost 49 Cents. By the time The Economist compiled the index, the cost of "Big Mac" was already 1,6 Dollars.
The first McDonald's in Moscow opened in 1990 year on Pushkin Square, then "Big Mac" cost 3 ruble 75 kopecks or 6 Dollars 18 cents at the official rate. In the United States, a popular burger was worth at that time 2 dollar.
Since then, economists have proposed using Big Macs to estimate the size of the gross domestic product. (GDP) and its share per person. This led to the emergence of a humorous section of the economy - "burgeronomics".
Despite the advantages of the Big Mac index, it has some limitations.. In many developing countries, eating on an international fast food chain like McDonald's is relatively expensive compared to local establishments., therefore, the demand for "Big Macs" is small.
Fast food chains use different strategies, adapting to a specific region, behavior and opportunities of buyers, accordingly, prices for the same product may vary greatly.
Many factors affect the cost of a McDonald's menu.: from production costs, delivery and rental before advertising costs, therefore, such an index is not suitable for assessing the economies of all countries in the world. And the burger itself has repeatedly changed in size and weight throughout its existence..
Besides, number of countries, suitable for assessing, directly depends on the presence of McDonald's there. For example, there is a "KFC index" in Africa, it is used for countries, where McDonald's is not represented, but you can purchase a branded chicken bucket from its competitor.
Every year The Economist presents the results of its index. For example, in 2011 year "Big Mac" cost in Russia 78 rubles (2,7 dollar), and in the USA - 4,07 dollar. This means, that the ruble was undervalued by 34 percent, and the dollar was supposed to be worth 18,5 ruble.
With 2011 the problem with the calculation of the index in India was solved. Hindus don't eat beef, which is part of the "Big Mac", a cow is a sacred animal for them. But according to the calculations of the compilers of the index, the price of meat is only 10 percent of the total cost, so for the calculations we chose a chicken burger - "Maharaja Mac". 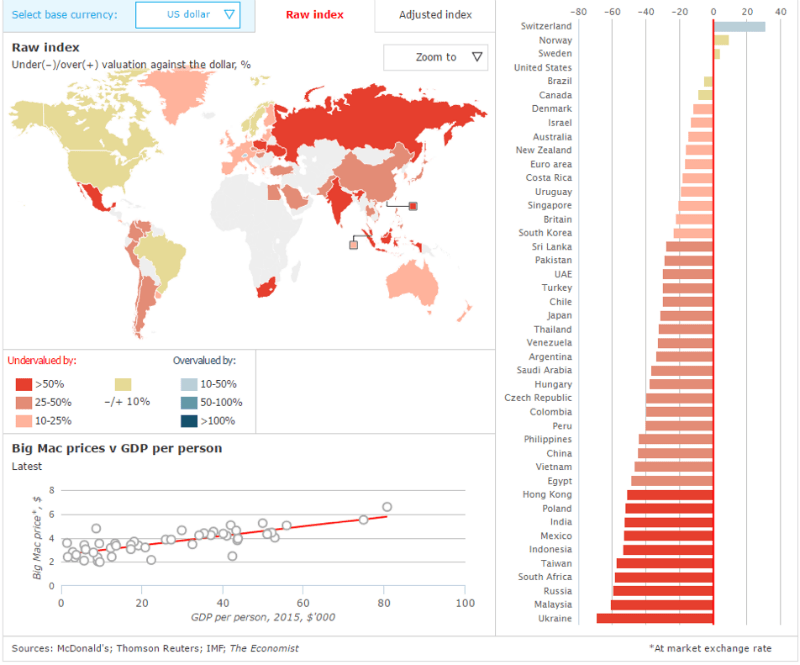
In July 2016 The Economist has updated the index again. According to the publication, the average price of a Big Mac in the USA in July was 5,04 Dollars, but in Russia - 130 rubles or 2,05 Dollars. That is, the ruble exchange rate is undervalued by 60 Percent, but in fact the dollar should be worth 25,79 rubles.
Thus, the ruble is one of the three most undervalued currencies in the world., yielding to Ukrainian hryvnia and Malaysian ringit. South African currencies were also included in the list of the most undervalued, Taiwan, Indonesia, Mexico, India, Poland and Hong Kong. In terms of "undervaluation" according to the Big Mac index, the ruble is far from being a champion. If in the USA the Big Mac costs $5,04, then in Ukraine, in terms of dollars at the official exchange rate, its price is $1,57. Consequently, hryvnia is undervalued by 68,8% and for a dollar they should not give 24,8, but only 7,74 UAH.
The other part of the rating contains overvalued currencies., the highest is the Swiss franc, according to the "Big Mac index" overestimated by 30,8 Percent, the top three also include the Norwegian and Swedish krona.
Burgeronomics was never conceived as an accurate way of measuring currencies, but rather as a tool to facilitate understanding of the theory of purchasing power parity. But the "Big Mac Index" has become the world standard, used in scientific works, and in his likeness, economists have made other "product" indices.
The Big Mac Index does not indicate, what exchange rate will be tomorrow. The real purpose of such indexes: be an indicator of what is happening in the economy, simplify understanding of exchange rates and indicate possible changes in the distant future.
Data 2015 of the year
IN 2015 the cheapest Big Mac can be enjoyed in Venezuela (three years ago, it was in this country that the most expensive Big Mac was) — for 0,67 dollar (underestimation of 86 %), потом идёт Украина — 1,55 dollar (-67,7 %), followed by India, where is the price for this sandwich 1,83 dollar (-61,7 %) and Russia (1,88 dollar). Самый дорогой Биг-Мак можно купить в Швейцарии — за 6,82 dollar (+42,4 %), затем идут Норвегия — 5,65 $ (+17,9 %), Швеция — 5,13 $ (+7 %) и Дания — 5,08 $ (+6 %). In other countries, Big Macs are sold cheaper, than in the USA, where does he stand 4,79 dollar. For comparison: in the so-called "euro zone" you will have to pay for this fast food product 4,05 dollar (3,70 euro in local currency), What's on 15,4 % less, than in the USA. All figures shown are based on the so-called "raw index" («Raw Index») for July 2015 of the year.
A source: Wikipedia, ITinvest