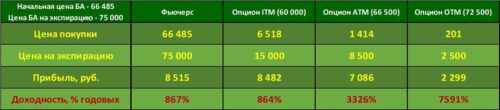
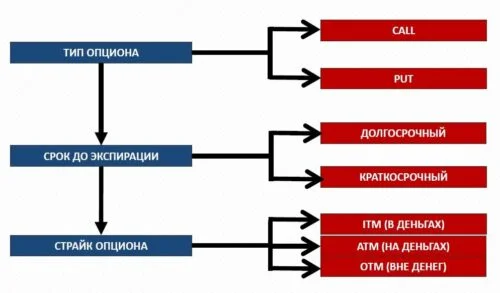
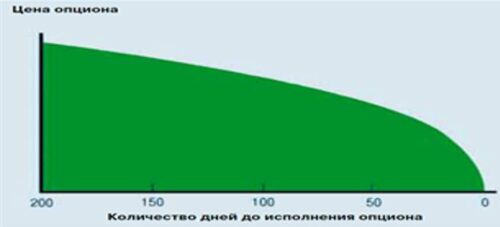
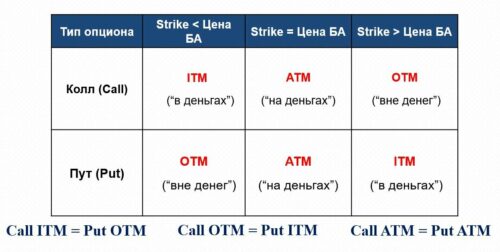
1. in money (ITM – in the money) For this option, its exercise allows you to either buy the asset cheaper, what is it on the market now, or sell it for more. Example: Futures on an ordinary share of Sberbank costs 14 000 rub. (100 Shares) – 120 Call (we have the right to buy shares at 120 rub.) And 160 Put (we have the right to sell shares at 160 rub.) 2. on money (ATM – at the money) The strike of this option is approximately equal to (closest) to the BA price. The so-called central strike (remember this concept, it will be used frequently). In this way, exercising this option does not give any advantage, because. the asset price on the market is approximately the same. 140 Call and 140 Put 3. out of money (OTM – out of the money) For this option, its execution is not profitable, because. does not allow you to buy an asset cheaper, what is it on the market now, nor sell it for more. In this case, it is easier to buy (sell) underlying asset in the market, than under the terms of the option. 160 Call and 120 Put Начинающие трейдеры очень часто неправильно думают, что если опцион ITM, then it is profitable, and if OTM is unprofitable. This is wrong. And here are two examples. Example 1. Let's admit, futures on an ordinary share of Sberbank costs 14 000 rub. …
LESSON 18. CLASSIFICATION OF OPTIONS DEPENDING ON STRIKE Read more