VTB (MOEX: VTBR) — the second largest Russian bank in terms of assets, which operates in almost the entire post-Soviet space. In the end 2020 of the year the company's banking business was present in 16 countries: Russia, Germany, United Kingdom, Georgia, Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan, Angola, Italy, China, India, Singapore, Bulgaria, Hong Kong and Switzerland.
VTB development stages
Creation.
IN 1990 the Bank for Foreign Trade - "Vneshtorgbank" - was established to service foreign economic operations of Russia. And already 2 January 1991 year, the financial institution received general license No. 1000 for the right to carry out all types of banking operations in Russia. IN 1994 Vneshtorgbank ranked 425th in the list of the thousand most capitalized banks in the world according to The Banker.
Reorganization.
IN 1997 year, the Central Bank of the Russian Federation reorganized the bank into an open joint stock company. IN 2002 year, the government bought the company from the Central Bank of the Russian Federation and appointed a new team of managers headed by the current president Andrei Kostin. Their goal is to turn the bank into a leading financial institution in Russia.
M&A-transactions, part 1.
To become the leader of the Russian market, Vneshtorgbank's management began to actively buy up competitors.
IN 2004 year purchased the bankrupt "Guta-Bank", on its basis, the retail bank Vneshtorgbank-24 was created the following year, who interacted with individuals and individual entrepreneurs and worked 24 hours a day.
IN 2005 the Industrial and Construction Bank of St. Petersburg was merged, with the help of it, Vneshtorgbank reached the leading position in the Russian banking services market.
IPO.
IN 2006 year "Vneshtorgbank" and "Vneshtorgbank-24" rebranded and changed their names to VTB and VTB-24. This abbreviation stands for External Trade Bank. IN 2007 year VTB conducted an initial public offering of its shares at 13,6 penny for paper, it became the largest international banking IPO in Europe at that time.
A crisis.
The collapse of the global financial system in 2008-2009 hit VTB hard, stock quotes fell below two kopecks. Nevertheless, the bank continued to develop even in such a difficult time.. IN 2008 VTB received a license to conduct banking activities in China and India, and also this year the management decided to consolidate the entire investment business of the group on the basis of VTB Capital.
M&A-transactions, part 2.
In 2010-2013, VTB continued to pursue an aggressive policy, buying up competitors, which allowed the group to grow several times in three years: assets increased in 2,4 Times, and the loan portfolio in 2,5 Times.
IN 2010 year from Russian Railways acquired "Transcreditbank", which later became part of VTB-24. IN 2011 VTB bought the Bank of Moscow and discovered big problems in the balance sheet, after which a criminal case was opened against the former shareholders. IN 2013 VTB created "Leto-Bank", who specialized in consumer lending in the mass client segment.
SPO.
IN 2011 year, the state additionally placed on the stock exchange 10% VTB shares in the amount 95,7 billion rubles. IN 2013 a year already VTB itself carried out an additional issue in the amount of 102,5 billion rubles among private investors, at that moment, the state's share decreased to 60,9%.
IN 2014 year the bank's management decided to convert the subordinated loan from VEB into new preferred shares of the first type in favor of the RF Ministry of Finance. IN 2015 VTB issued second type preferred shares, which were placed by closed subscription in favor of the Deposit Insurance Agency as part of the program for additional capitalization of the bank through OFZ. After which the share of the state increased to 92,2%.
Present time.
IN 2016 year on the basis of "Leto-Bank" created "Post-Bank", which uses a huge base of post offices. IN 2018 year in order to increase the efficiency of VTB-24 merged with VTB. IN 2019 VTB acquired three more banks: "Renaissance", Zapsibkombank and Sarovbusinessbank.
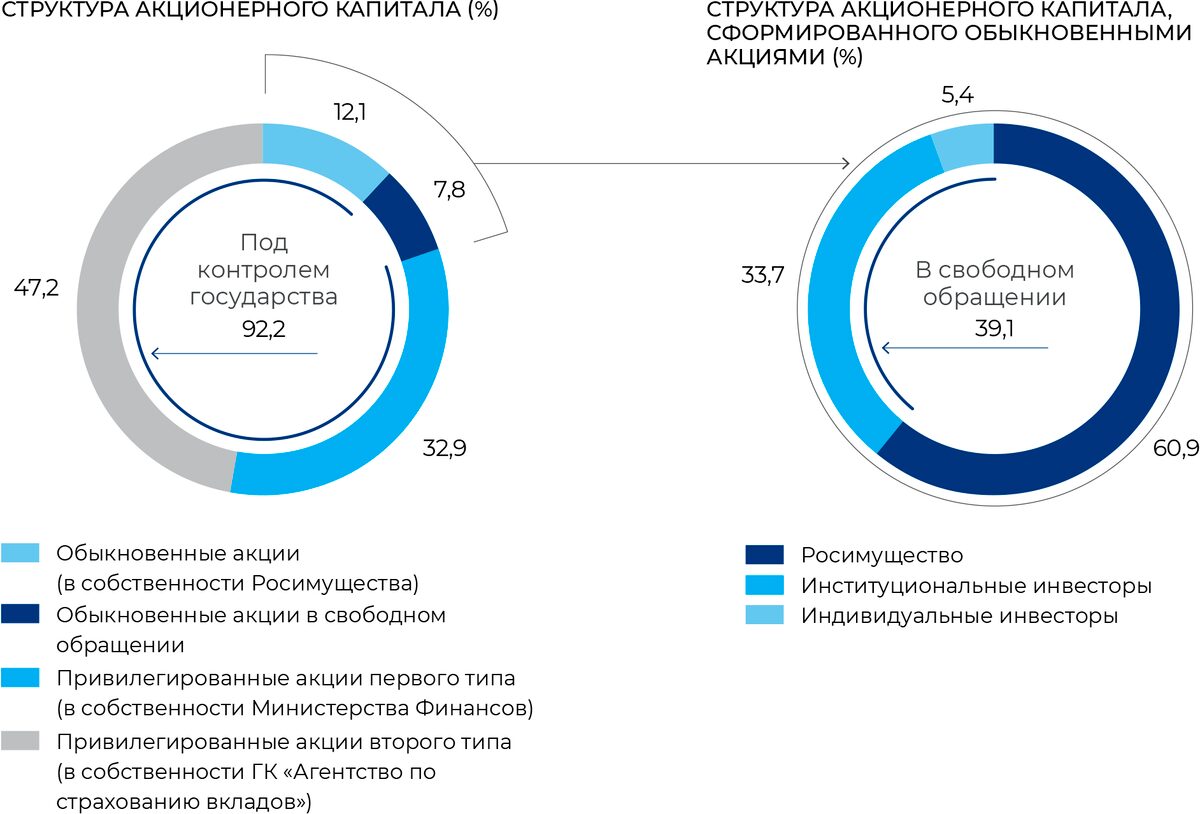
VTB shareholder structure
The company has three types of shares in its authorized capital: ordinary and preferred two types.
Authorized capital
| Type of shares | Number of issued shares | nominal value |
|---|---|---|
| Ordinary shares | 12 960 541 337 338 | 0,01 R |
| Type 1 preference shares | 21 403 797 025 000 | 0,01 R |
| Preferred shares of the second type | 3 073 905 000 000 | 0,1 R |
VTB shareholder structure
| Shareholder | Type of shares | Share in authorized capital |
|---|---|---|
| Deposit Insurance Agency | Preferred shares of the second type | 47,2% |
| Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation | Type 1 preference shares | 32,9% |
| Rosimushchestvo | Ordinary shares | 12,1% |
| Free-float | Ordinary shares | 7,8% |
VTB Business Plan for 2019-2022
Bank strategy up to 2022 year assumes that the company will reach the following financial targets:
- ROE — 15%.ROE — 15%.
- Dividend payout ratio - 50% net profit.
- Net profit - 310 billion rubles. Net profit - 310 billion rubles.
Besides, VTB management presented its forecasts of the company's net profit:
- For 2021 year - For 2021 year - 295 billion rubles.
- For 2022 year - 310 billion rubles.
- After 2022 of the year - +10% annually.
VTB dividend policy
Bank allocates 50% net profit under IFRS on dividends based on the principle of equal dividend yield for all three types of shares.
Dynamics of past dividend payments
| Dividend on 1 common share (AO) | Payout ratio from net profit | |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 0,00117 R | > 100% |
| 2016 | 0,00117 R | > 100% |
| 2017 | 0,0034 R | 61% |
| 2018 | 0,00109 R | 15% |
| 2019 | 0,00077 R | 10% |
| 2020 | 0,0014 R | 50% |
Dynamics of future dividend payments
| 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dividend on 1 common share | 0,0063 R | 0,0071 R | 0,0083 R |
| Dividend yield | 13% | 14,8% | 17,3% |
| Net profit, billion | 295 | 310 | 341 |
| Average annual market price of ordinary shares | 0,05 R | 0,06 R | 0,07 R |
Comparison with competitors
| P / E | P / BV | ROE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| VTB | 5,93 | 0,61 | 18,5% |
| Sberbank | 6,74 | 1,45 | 25,3% |
| Bank "Saint-Petersburg" | 2,45 | 0,38 | 16,1% |
| TCS Group | 24,18 | 9,12 | 38% |
Arguments for VTB
Growth in net profit and dividends. In case of successful implementation of the business plan, VTB will pay record dividends in the next three years.
Evaluation. Compared to its main competitor, Sberbank, it looks unreasonably low.
High customer loyalty. VTB ranks second in this indicator with a result in 74%.
Growth of the Russian economy. As of July 2021 the Bank of Russia predicts, that the GDP growth rate will be:
- in 2021 year 4-4.5%;
- in 2022 year 2-3%;
- in 2023 year 2-3%.
Arguments against VTB
Payout risk less 50% net profit. VTB previously deviated from the principle of allocation for dividends 50%. IN 2018 year - due to the transition to the Basel 3 standard, resulting in the need for additional capital, and c 2019 year - with the onset of the economic downturn due to COVID-19.
Capital adequacy. The bank plans to pay dividends for 2021 a year in two tranches: in 3 And 4 quarter 2022 of the year. The main reason is the heavy burden on capital, which does not allow VTB to pay all dividends at once.
What's the bottom line?
VTB's valuation is quite far behind Sberbank. This is mainly due to poor results. 2020 years and low dividends for this period. But already in 2021 the situation may change dramatically, if the second largest bank in Russia in terms of assets manages to fulfill its forecast for the current year: net profit — 295 billion rubles, net profit distribution ratio under IFRS — 50%.
VTB is suitable only for investors with strong nerves, who are willing to take a certain risk for the sake of high profitability. The bank can show dividends in the next three years 45%.