
Protecting and maintaining the integrity of the market is achieved by government agencies and the joint efforts of four key groups (SEC, NASD, SIPC and FOMC), which together form then, what's in the stock market – regulating pyramid.
Nobody regulates themselves so rigidly and thoroughly, how stock market. Strict standards and requirements for professional bidders, an extensive system of regulatory services of the US authorities – all these are measures of control over the activities of participants.
USA congress.
Congress nominates members to the Securities and Exchange Commission and is responsible for its effective functioning. He is also responsible for legislative activities in the securities market and for the formation of such new organizations in the stock market., how “Organization of investor protection in the stock market”.
SEC – Securities and Exchange Commission.
The legislative, the controlling and registering body in the US securities market is the US Securities and Exchange Commission (U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission – SEC).
Legislative regulation of the US securities market began in 1933 year since the adoption of the Law on Securities (Securities Act of 1933).
NASD – National Association of Brokers-Dealers of the USA. Operates under the supervision of the SEC.
Its main functions:
- registration, issuance of licenses, regulation and supervision of all broker-dealers in the USA;
- electronic exchange system management.
- at the slightest violation of the stock exchange regulations, NASD may “delete” from the market of any certified specialist or even an investment company, taking the case to court.
IN 1996 G. NASD was restructured and two subsidiaries created:
- NASD Regulation, Inc., which regulates and supervises broker-dealers.
- Тhe Nasdaq Stock Market, Inc., responsible for regulating the electronic exchange system.
Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC).
In order to protect investors from bankruptcies of brokerage and dealer firms in 1970 year, by a special act of Congress, the Investor Protection Corporation was formed (Securities Investor Protection Corporation). Corporation – non-profit organization, whose fund is formed by contributions from members – securities companies (broker-dealer firms). Of the seven board members, five are appointed by the President of the United States., one - by the Ministry of Finance, one - by the Federal Reserve Board (Federal Reserve System – FRS). SIPC is required to submit an annual report to the SEC, last, in its turn, has the right to inspect its activities and make adjustments to the rules of its work. Most of the registered brokers and dealers are members of the SIPC. The law provides financial protection for brokerage accounts with securities and money on them in the event of liquidation of a broker company. In this case, the court-appointed manager or SIPC can arrange for the transfer of the client's funds to another company that is a member of the SIPC.. If this is not possible, SIPC protects the user as follows:
- Client receives securities, owned by the liquidated firm and registered in his name and not negotiable. The rest of the securities are distributed among clients on a pro rata basis.
- If the company in liquidation does not have enough resources to meet all the client's requirements, SIPC satisfies the remaining requirements for the amount $500 thousand, of which there can be no more than cash $100 thousand.
- If the client remains dissatisfied in this case, then he receives, in proportion with other creditors, a share from the sale of the remaining assets of the bankrupt.
The time for SIPC to satisfy customer claims depends on the size of the company being liquidated and the circumstances of the liquidation.. SIPC protects the investor only from the financial insolvency of the broker firm, but not from market fluctuations in the value of the investments themselves.
FOMC (Federal Open Market Committee) – The Federal Open Market Committee was organized in accordance with the Banking Law 1935 years to replace the Open Market Policy Association (OMPC).
The Committee includes seven members of the Board of Governors and the presidents of five reserve banks. Deals with the purchase and sale of federal debt and US Treasury securities. FOMC meets eight times a year. At each meeting of the Committee, a vote is taken on the size of the interest rate, the current economic situation is discussed, direction of monetary policy, etc.. The minutes of the meetings are published three weeks after the meeting., which summarize the main results of the meeting. FOMC is part of the Federal Reserve System.
Federal Reserve System (FED)
Federal Reserve System (FRS, the Fed) – system, established in 1913 G., serves as a guide to US monetary policy, analogue of the central bank. FRS includes: US President-appointed FRS Board of Governors, Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), twelve regional Federal Reserve Banks, fiscal agents of the U.S. Treasury, numerous private banks, and a variety of advisory tips. Congressional decision provides for an independent position of FRS in the US government, which relieves her of everyday political pressure. Independent of Congress in terms of funding and administrative control, FRS is accountable to Congress.
The independence of FRS is a consequence of three structural features:
- procedures for appointing managers,
- procedures for appointing presidents of Federal Reserve Banks,
- nature of funding.
The governing body of FRS is the Board of Governors composed of 7 members of. Each member of the Council is appointed for a term of 14 years with the right to renew. The FRS Act provides the President of the United States with the right to fire any FRS governor. The Board of Governors is chaired by the Chairman and his Deputy. Subordinate to the Board of Governors 12 FRS regional offices, called “Federal Reserve Banks”. Regional offices are geographically located in 25 branches and exercise their powers in the states assigned to them, named after those cities, where their headquarters are located.
List of Federal Reserve Banks:
- Federal Reserve Bank of Boston
- Federal Reserve Bank of New York
- Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia
- Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland
- Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond
- Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta
- Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago
- Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis
- Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis
- Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City
- Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas
- Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco
The president of each Federal Reserve Bank is appointed for a five-year term by the bank's Board of Directors, after which this appointment is subject to final approval by the FRS Board of Governors.
Independent of Congress in terms of funding and administrative control, FRS is accountable The Congress.
Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), key organ, monetary policy manager. Its decisions are aimed at stimulating economic growth while maintaining the stability of prices and monetary circulation.. Determines the level of interest rates in the country. The voting rights in the committee belong to 7 the manager of FRS and 5 representatives of regional offices, delegated on a rotational basis.
In addition, individual exchange transactions, significantly affecting various parts of the financial market, also monitored FED.
For instance, the amount of margin coverage is legally fixed by the Federal Reserve on a nationwide scale at a fairly high level. The purpose of this is to eliminate the negative impact of margin operations on the credit market.. So, instruction “T” (regulation Т) requires, so that the initial guarantee fee (margin), made mandatory with 1975 G., was at least 50% purchase price.
The analogue of this instruction in the banking sector is the rule “U” (regulation U), determining the size of the loan, which the bank can issue to the client for the purchase of securities. Only the most reliable securities are allowed for margin operations today: stock, registered and quoted on national exchanges, and government securities.
Operations with government securities are of great importance in the USA, ie. with government commitments, in the system of monetary regulation of the economy. However, there is one essential feature: government securities never dominate the markets over private, corporate (this rule also applies to other developed countries). Extremely developed secondary market for government securities in the United States contributes to the successful fiscal and monetary regulation of the economy: the entire state budget deficit is covered only by issuing government debt, and the Fed's operations on the open market, introduced since the late 1930s, allow you to constantly adjust the size of the money supply.
- Corporate securities are represented by private short-term and long-term bonds.
- Short-term liabilities include commercial paper (commercial paper) and certificates of deposit (certificates of deposit).
- Commercial unsecured bills of exchange from private firms are issued with maturities from 3 to 270 days (average circulation period – 30-35 days), therefore their aftermarket is limited. Placement of commercial papers is carried out by investment banks, and only reputable companies have access to this market, closely related to such banks.
- Certificates of Deposit are evidence, certifying the making of a term deposit with a credit institution. They are issued by large commercial banks, have a coupon system for paying interest, purchased by non-financial corporations as a means of placing temporarily surplus funds.
- Long-term securities include stocks and bonds.
- Distinguish between simple, or ordinary, stock (ordinary, common stocks) and privileged (preference stocks). Common Shares in Profit Distribution, with participation in management, and also in the case of distribution of property in bankruptcy have ordinary rights. Preferred shares, when receiving a dividend or dividing property, provide their owners with certain advantages.
- The share of debt in the structure of financial assets of American corporations has significantly increased (bond loans).
-
IPO – Investment banks are engaged in the initial placement of securities.
-
Secondary turnover of shares is split into exchange and OTC.
Each exchange sets its own requirements for accepting securities, but, as before, the standard of rigor here is the New York Stock Exchange. With 1982 years, its requirements for issuing companies have tightened. To be admitted to the exchange, you must have an annual income of at least 7 million. Doll.; market price of shares, owned by shareholders, should be at least 16 million. Doll.; company property value – at least 16 million. Doll.
As a result of the development of information technology, a single information network has emerged, uniting all exchanges and the most organized part of the over-the-counter turnover – stock exchange without a trading floor (NASDAQ).
Nowadays the prestige of NASDAQ has gotten so high, that individual companies, even reaching indicators, satisfying the requirements NYSE, remain in NASDAQ. In this way, in stock trading over-the-counter turnover complements exchange trading and even competes with it.
Although the high share of equity capital as a source of financing for the economy is a national feature of the United States, the stock market has not been the main segment of the stock market for a long time. Currently, the value of bonds in 1,3 times the value of shares (for example, in Germany in 10 once). Bonds are the main instrument of corporations to raise financial resources in the stock market.
With the advent of new types of releases, such, like zero coupon bonds (zero coupon bonds) and junk bonds (Junk bonds), the bond market began to change. Investing in bonds began to lose its reliability. Regular interest on zero-coupon bonds is not paid now, and this increases the risk. However, as the maturity of the grain coupon approaches, an invisible accrual of interest occurs.. Greater risk is offset by higher returns. This is true for investing in junk (“garbage”) bonds, having the lowest investment rating. This is why American Brokers talked about transforming the bond market from “a quiet backwater in a casino”.
OTC market – pink sheet.
The most important feature of the American bond market is its predominantly over-the-counter nature., and turnover of government securities on 99% is over-the-counter. The growing importance of OTC markets in modern conditions is associated not only with their decisive role in the initial offering of securities and in the trading of debt instruments..
In modern American practice, in the structure of over-the-counter turnover, it is customary to distinguish “the third” (third market) And “fourth” (fourth market) markets. “The third” And “fourth” OTC markets, focused exclusively on institutional investors, and at the same time they are very capacious. The trend towards institutionalization of financial markets has been traced in America for a long time, as a result, institutional investors currently own 1/3 all securities.
Derivative financial instruments (derivatives). In the US stock market, the importance of institutional investors has grown quite actively; their share in derivatives trading is 65%, and individual operations (such, like index futures) focused exclusively on insurance of large portfolios. Derivative trading originated in the United States (and for the first time in the world) in the mid 70s. Currently, the volume of the derivatives market has reached this size (the annual cost of contracts in 2 times GNP), what is already being said in America about a special branch of the financial industry (a kind of management of the emerging financial market Managed Futures), which is designed to professionally manage investments in derivatives.
The modern commodity futures exchange has become universal (by the list of objects of trading) institution. It retains its original product specialization (agricultural, oil) and at the same time has sections of currency futures (precious metals and foreign currency), financial futures (interest rate and index contracts), options. As transactions with financial contracts significantly prevail over futures trading, then the distinction between commodity and stock exchanges loses its meaning.
Radical shifts, which occurred and continue to occur in the movement of loan capital, in general in financial markets, contributed to the growing volatility of situations in the world, regional and local exchanges. Going in due time to “floating” currencies increased the likelihood of currency risks. The Fed's refusal to regulate interest rates required insurance of those risks, which were associated with fluctuations in short-term interest rates.
New hedging strategies have appeared on the securities market, and derivative transactions have become widespread. In particular, derivatives contributed to the adaptation of the stock market to the changed conditions, becoming the fastest growing and most dynamic segment.
Changes in the regulation of the government securities market in the 1990s (in particular, placement of the overwhelming majority of liabilities among non-bank investors) allowed the federal government to mitigate the impact of budget deficits on the expansion of money circulation. The rise in government debt never led to an increase in market interest. There was also no deterioration in the conditions for financing private capital investments.. The increase in government borrowing was combined with an intensive expansion of private lending operations. Accordingly, government debt has ceased to be seen as a priority problem of the economic policy of the US government..
US banking regulators
Banks in the United States are subject to federal or state regulation. The bank can obtain a federal license (National Bank), and then its activities will be regulated by federal law without taking into account any state regulations. Bank can get a state license (staff bank), and then its activities will be formally regulated by the laws of the state, but to a large extent also by federal laws.
It means, that the US banking system is a dual reporting system, dual regulation. At the same time, banks themselves choose their jurisdiction.. The choice depends on, whether the bank intends to open a branch bank. The question of opening branches in the United States is entirely up to the state authorities, regardless of whether, is the bank national or state.
The preservation of the dual subordination system in the US banking system is largely associated with historical traditions and that socio-political role, played by small banks in rural areas. For example, in Texas, in almost every small- the city has the First National Bank; most of these banks were formed in the 19th century. These are banks of federal jurisdiction. But along with them, banks of state jurisdiction operate quite successfully in the same cities., and the smaller the town, the more the bank plays in it. The main U.S. banking regulators are:
at the federal level (cm. rice. 2.2);
- at the state level:
- state law;
- state banking department.
- The second tier of the US banking system is:
- national banks (banks of federal jurisdiction), are members of the Fed;
- regular banks:
- full-time banks - members of the FRS; full-time banks are not members of the Fed;
- bank holding companies;
- international financial institutions (IBRD, etc.).
- By the nature of the activity, according to the main areas of operations, US commercial banks can be divided into several groups:
- bank holding companies;
- universal commercial banks;
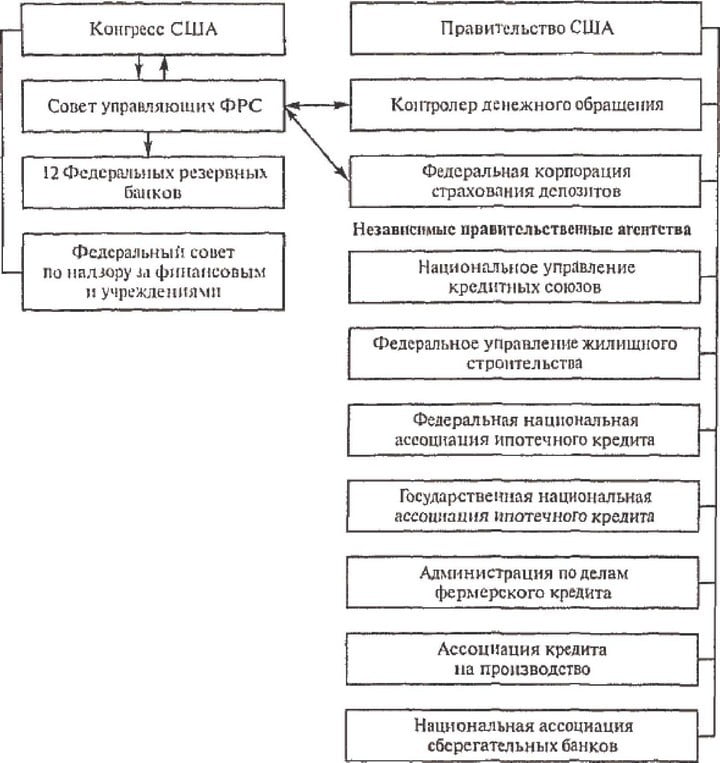
Rice. 2.2. The structure of the regulatory bodies of the US banking system at the federal level
- consumer credit banks;
- farm loan banks;
- Edge corporation;
- international banking institutions;
- specialized mortgage banks;
- housing banks;
- mutually saving banks,
- Beyond banks in the US financial market, competing with banks in terms of attracting resources, and in active operations, various non-banking institutions operate, incoming, but, to the banking system:
- savings and loan associations (construction, loan, loan-saving);
- financial companies;
- credit unions;
- mutual housing associations;
- production credit associations;
- investment companies.
In the end 1998 G. in the USA there were about 8,8 thousand. commercial banks, What's on 40% less, than in 1989 G., on 1 January 2001 G. their number was a little over 8,3 thousand, and on 1 June 2002 G. — 7996. The reduction in the number of banks is mainly due to mergers and acquisitions; the number of bank liquidations as a result of bankruptcies is quite insignificant. Effective surveillance system in place in the United States, primarily by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, allows you to carry out bank reorganization measures, without bringing them to bankruptcy proceedings.
The state, represented by government bodies, exercises control over the functioning of the entire financial and credit sphere. The government bodies exercise control over the functioning of the banking system, performing the following functions:
- issuance of permits (charters) to open banks and branches. The charter includes a license, registered articles of association and bank establishment agreement, activity brochure;
- issuance of merger permits (absorption) banks;
- issuance of liquidation permits;
- issuance of instructions based on current legislation;
- checking the activities of banks and monitoring the elimination of deficiencies;
- synthesis of reporting and statistical materials;
- advising bank management;
- closure of insolvent banks, capital adequacy ratio of which is less 2%.
Every major bank is audited 4-6 times a year by each of the main regulatory bodies - the District Federal Reserve Bank, Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, Money controller. Collective checks prevail, when the leader (initiator) becomes each of the regulatory authorities in turn, but they check everything together.
The main government regulatory bodies of the US banking system are the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency and the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation..