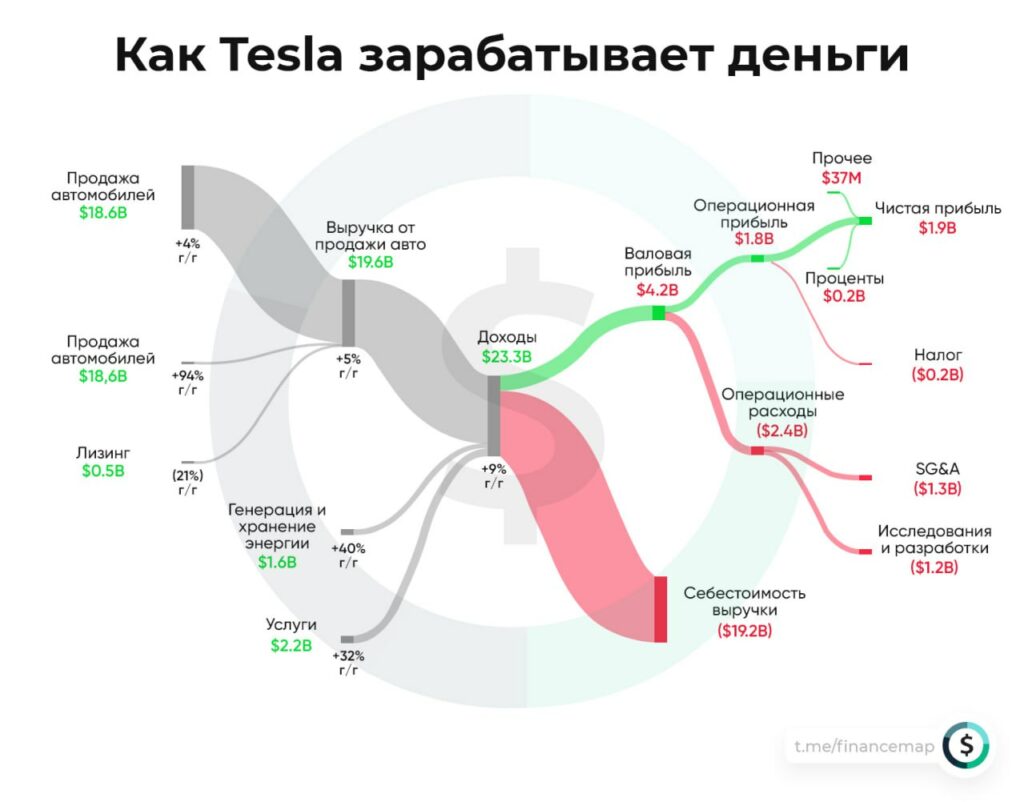
I decided to write a small FAQ for investors who decided to invest money in trust management to a private trader ie. to me. You can find out more details by contacting me. @Good_trades
Conditions:
Trading is currently carried out only on the US stock market(NYSE, NASDAQ, AMEX) shares and ETF inside the day, without transferring positions to the next day.
Recommended amount: from 30 000$ (minimum 10 000$)
To whom the account is opened: only for the investor. Only you can replenish / withdraw funds
Broker: I recommend for accounts over 30000$ (individually from the amount)
Duration: from 6 Months
Withdraw funds: individually(not more often 1 once a month)
Yield: average 3-10% per month (depends on the amount, broker leverage, market conditions, etc.)
Risks: 5-10% maximum total risk for the entire deposit.
Profit distribution: 50% on 50% (individually)
An agreement is signed with an investor.
Contacts : Skype: nysetrade
Telegram: @Good_trades
Trust management
Trust management (DU) - service, provided by management companies or banks in the securities market.
In case of trust management, the client transfers funds or other assets to the management company under an agreement. She carries out transactions on her own behalf, but in the interests of the client, for which he receives remuneration as a part of the earned profit or as a percentage of the value of assets, under management. Trustees in most cases cannot guarantee profitability, which depends on the economic environment.
Trust itself means, that we transfer our assets to the manager at the disposal, but without transferring property rights to him. This implies, that professionals will work with the assets, have the appropriate qualifications and time to carry out transactions with assets in order to generate profit for the client of trust.
Assets, which can be transferred to trust management, can be completely different. These can be real estate objects, cash, securities, as well as various tangible and intangible assets. In general, the process of trust management is regulated by the Chapter 53 GK RF.
Individual trust management
In this case, the investor's funds are managed on a personal level.. An individual trust agreement is concluded with a trust client, which is regulated by the civil code of the Russian Federation. As an annex to the contract, a personal investment declaration, where the main parameters of investments are reflected (a little further we will indicate which ones). The contract and personal investment declaration serve as protection against unauthorized actions of the manager. At the same time, from the point of view of legislative regulation, there are practically no restrictions on the actions of the manager.. And unlike mutual funds, any investment strategy is theoretically feasible here, that is, any assets, starting from the derivatives market, ending with foreign sites. Any strategies are also possible., ranging from classic passive investing to speculative strategies with robots, algorithms, etc.. Conditions for investment amounts, terms and potential risks are already discussed here individually.
Also important, that the manager is not entitled to guarantee at least any profitability, if it is done, then this can be equated with a violation of the law. Here we can only talk about the degree of probability of obtaining the expected return. Since profitability and risks are always proportional, then according to conservative strategies the probability of obtaining the expected profitability is much higher than according to aggressive.
Consulting asset management
Consulting is not a real fiduciary, since in this case the right to dispose of assets or monetary funds does not pass to the manager, and all transactions take place on behalf and on behalf of the client himself. The investor only has the right to heed the advice of a more experienced market participant or not.
In the case of a brokerage advisory office, this is a service, which was created by the brokers themselves and (in our personal opinion and suspicion) often conflicts with the interests of clients, since the frequent change of investment ideas encourages the client to make more transactions and, as a result, pay a large brokerage commission (cm. article "why brokers don't like investors").
Who manages the assets
In this case, a consulting management agreement is concluded with the client., in which it is written, that all transactions are carried out on behalf of and on behalf of the client and all responsibility lies entirely with him.
Who can take money for management
First of all, it should be said about, who is entitled to engage in official trust management in the securities market. Trust management can only be carried out by organizations, who have a specialized license to carry out activities for the management of securities. Such organizations are called management companies.. And directly employees of these management companies must have special certificates of the Federal Financial Markets Service, certifying the employee's right to manage securities and funds. Only in this case, it will be a legally regulated and formalized trust process.
This norm is governed by article 5 “Securities management activities” FZ “About the securities market”.
Types of trust management
Currently, the concept of trust management has largely received a free interpretation.. As it happens, that trust management means various forms of consulting and analytical services.
That's why, let's look at what are the main forms of trust management today and what are the mechanisms of their work. Can be distinguished 3 main forms of trust management:
- Collective trust management.
- Individual trust management (classic trust management).
- Consulting trust management.
How collective trust works
The main feature is that, that investors' funds are pooled into large pools and the manager manages the entire pool, and shareholders own only a fraction of this pool (share) and receive a proportional income. In other words, one might say, that it is a retail form of trust available to small customers.
Trust management (private trader)
Trust management (private trader) is one of the investment options, which allows you to delegate the management of your investments to professionals. In this article, we will look at the concept of trust management, Its advantages, Principles of work, And also let's talk about that, How to choose a reliable private trader.
What is trust management??
Trust management is the process of managing an investor's assets by a private trader or investment company. Owner of funds (investor) outsources the management of their investments to a professional, who makes decisions on his behalf. Trust management can include different types of assets, Such as stocks, bonds, Real estate and other financial instruments.
Advantages of trust management
- Asset Diversity: Trust management allows you to invest in various assets, which contributes to portfolio diversification and risk reduction.
- Professional management: Private traders have experience and knowledge in the field of financial markets, which allows them to make informed investment decisions.
- Risk allocation: Trust management helps to distribute risks between different assets and strategies, what can reduce the impact of adverse situations on investment.
- Minimizing emotional decisions: Private traders base their decisions on market analysis and fundamental factors, which helps to avoid emotional reactions to short-term market fluctuations.
How does trust management work??
Trust management includes several stages, which are usually performed by private traders:
- Asset Management Process: A private trader conducts market analysis and selects suitable investment opportunities.
- Risk and Return Assessment: The trader assesses the potential risks and the expected return on investment.
- Making investment decisions: Based on analysis and evaluation, The trader makes decisions on the allocation of assets and the choice of specific investments.
- Portfolio monitoring and rebalancing: A private trader monitors the performance of the portfolio and makes adjustments if necessary to achieve investment goals.
How to choose a private trader?
Choosing a reliable private trader is an important step in deciding whether to use trust management. Here are some tips, that can help you make the right choice:
- Research & Evaluation: Conduct market research and evaluate the different trust management options. Study professional ratings and reviews from other investors.
- Reputation and experience: Check the reputation and experience of the trader. Learn, how many years the trader has been working in this field and what results he has achieved.
- Portfolio & Performance: Examine the trader's portfolio and performance over previous periods. Make Sure, that its strategy aligns with your goals and risks.
- Cost of services and commissions: Specify the cost of services and the trader's commission. Understand, what payments you will have to make and how it can affect your profitability.
Key factors for successful trust management
To achieve success in trust management, It is important to consider the following factors::
- Purpose and risk tolerance: Define your investment goals and determine your risk appetite. This will help you choose the right strategy and trader.
- Long term strategy: Trust management is aimed at achieving long-term goals. Make Sure, that your trader has a clear strategy, relevant to your investment goals.
- Diversification: Distributing investments across different assets and markets will help reduce risk and increase portfolio stability.
- Regular monitoring: Determine the frequency of monitoring your portfolio and communicating with the trader. Regular analysis will help you evaluate the effectiveness of trust management and make the necessary adjustments.
Risks and limitations of trust management
When using trust management, the following risks and limitations should be taken into account::
- Market volatility: Financial markets can be subject to significant fluctuations, What can affect the profitability of the portfolio.
- Possible losses: Investments always carry the risk of losing part or all of the invested funds. No guarantee, that trust management will bring profit.
- Conflict of interest: Private traders may be asked to invest in certain assets or products with a certain commission, What can create a conflict of interest with the investor.
- Limited control: When using trust management, the investor has limited control over the decisions made and asset management.
Tips for choosing a trustee
When choosing a trustee, consider the following tips::
- Defining Your Goals: Be clear about your investment goals and risk tolerance. This will help you choose a trader, that fits your needs.
- Search for recommendations and references: View ratings and reviews of traders. Reach out to professionals in the financial industry for guidance.
- Face-to-face meeting and interview: Meet potential traders in person or have an interview by phone/video. Ask them questions about their experience, management strategies and process.
- Verification of the license and regulator: Make Sure, that the trader has the necessary licenses and regulatory approvals to carry out trust management.
Strategies and approaches in trust management
Various strategies and approaches are used in trust management, which can be tailored to the investment objectives of individual clients. Some common strategies include::
- Conservative approach: Strategy, aimed at preserving capital and moderate growth. It mainly invests in stable and low-risk assets.
- Aggressive approach: Strategy, aimed at maximizing profitability and ready to take high risks. Invests in assets with high return potential, but also at great risk.
- Passive investing: Strategy, based on the repetition of the performance of a particular market index. Uses passive investment funds, such as ETFs.
Investing in trust management
Investing in trust management usually requires a minimum investment amount, which may vary depending on the trader or company. Some traders may offer to invest amounts ranging from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars or more.
Important to consider, that the results and return on investment in trust management may vary depending on the chosen trader and his strategy. It is recommended to familiarize yourself with the past results and performance of the trader, to make an informed decision.
Examples of successful trust management
There are many successful traders and investment companies in the market, providing trust management services. It is important to study their performance and reputation, To choose a trader, appropriate for your goals and risks.
For example, “XYZ Foundation” for the latest 5 years reached an average annual yield of 10%. Their strategy includes broad asset diversification and active portfolio management. They have positive feedback from clients and a reputation as a successful trader..
Regulation of trust management
Trust management is regulated by the laws and regulators of financial markets. Regulators usually require, that traders and investment companies have certain licenses and permits to provide trust management services.
This helps protect the interests of investors and ensure that traders comply with certain standards and regulations.. Besides, traders and companies, providing trust management, must provide reporting and information on their activities to ensure transparency and openness.
Trust management vs. self-trading
Trust management and independent trading have their own characteristics and advantages. Let's take a look at some of the differences between them.:
- Differences and benefits: Trust management offers professional investor portfolio management, based on the knowledge and experience of traders. Self-trading requires independent decisions and market analysis.
- Time costs and expertise: Trust management allows the investor to focus on his other affairs, as the trader takes over the management of the portfolio. In the same time, independent trading requires time and expertise to analyze the market and make decisions.
- Risks and returns: Trust can help reduce emotional reactions and spread risk across different assets. Self-trading can be more flexible, but also involves more risk.
Conclusion
Trust management (private trader) gives investors the opportunity to delegate the management of their investments to professionals. It has a number of advantages, such as variety of assets, professional management, risk sharing and minimization of emotional decisions.
When choosing a trustee, it is important to consider your goals, conduct research and evaluation, as well as check the reputation and experience of the trader. Regular monitoring and evaluation of the chosen strategy will help to achieve successful trust management.
Questions and answers
- What are the main benefits of trust management?
- Key Benefits of Trust Management Include Diversity of Assets, professional management, risk sharing and minimization of emotional decisions.
- How to choose a reliable private trader?
- Research is recommended to select a reliable private trader, evaluate the reputation and experience of a trader, study his portfolio and performance, as well as learn about the cost of services and commissions.
- What are the risks associated with trust management?
- Trust risks include market volatility, possible losses, conflict of interest and limited investor control.
- What is the minimum amount of investment in trust management?
- The minimum amount of investment in trust management may vary depending on the trader or company, and usually amounts to several thousand or tens of thousands of dollars.
- What strategies are used in trust management?
- Trust management uses different strategies, such as the conservative approach, aggressive approach and passive investing, depending on the investment objectives and risk tolerance of the client.